Finkelstein Reaction
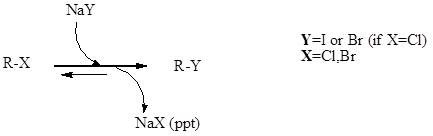
Finkelstein reaction is a single step substitution nucleophilic bimolecular reaction (SN2) which involves the halide replacement. The reaction was discovered by Hans Finkelstein a German chemist. It is a type of equilibrium process and it is carried forward as acetone has poor solubility for formed metal halide which involves Le Chatelier’s principle. The reaction is […]
Eschweiler- Clarke Reaction
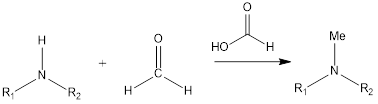
Eschweiler- Clarke reaction is a substitution organic chemistry reaction which leads to the formation of tertiary methylamines by reaction of primary amine or secondary amine in presence of formaldehyde and formic acid. The reaction was discovered by German chemist Wilhelm Eschweiler as well as British chemist Hans Thacker Clarke. Mechanism of reaction– Firstly in reaction […]
Baylis-Hillman Reaction
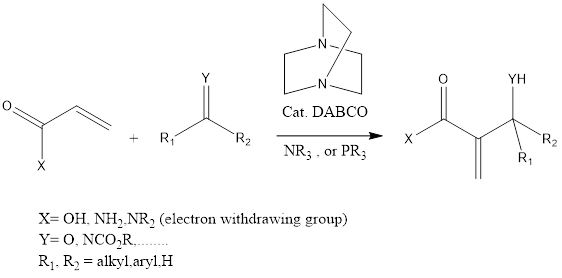
Baylis-Hillman reaction is a coupling organic chemistry reaction which leads to forming C-C bond in between α, β carbonyl compounds like aldehyde or activated ketone and electrophiles. The reaction takes place in presence of tertiary amine and phosphine and mostly DABCO (1,4 Diazabicyclo [2.2.2] octane tertiary amine is used. The reaction has been discovered by […]
Rational Drug Design

It is a process of discovery of a new molecule depending upon the target receptor. Generally, the drug is a small organic molecule that shows its action either by potentiation or inhibition of biomolecules that are present in the human body. While designing a molecule it is very important to take care of its shape […]
Bio-organic Chemistry
It deals with two fields biochemistry and organic chemistry. The biochemistry part deals with living processes using the chemistry of molecules. This stream tends to increase organic structure, properties of molecules, and synthesis knowledge towards biological phenomena. History: Dr. Margret was the first person who discovered the amino acid term when she was trying to […]
Hybridization
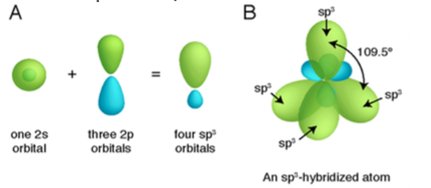
Hybridization is defined as the mixture of two different molecular orbitals to form a new orbital/hybrid having different energy and shape. Types: Sp, Sp2, Sp3, Sp3d, Sp3d2, Sp3d3. Sp hybridization: It is done by intermixing one ‘s’ and one ‘p’ orbital. Finally, originated hybrid has an energy of two different orbitals and hybrid is called […]
Combinatorial Chemistry

Definition: It is a method of preparation of a large number of compounds in a single process, libraries can be made either as a mixture or individual compounds which are developed by computer software. Techniques that are utilized for the identification of library components. These can be used for different fields. History: It is not […]
Carbohydrates

Carbohydrates are made up of three basic compounds that are oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. Hydroxyl functional group is present whereas suffix -ose represents the sugar part. These are the derivatives of polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. Most of the carbohydrates are abundantly found and are the source of energy. These are classified into the following types: […]
Lipids
Lipids are the heterogeneous compounds which are made up of fatty acids. Lipids are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents like chloroform, ether, benzene, etc. These are nonpolar in nature. These are classified as waxes, glycolipids, acylglycerols, terpenoids, and sphingolipids. History: Lipids are regarded as a major concentrated storage form of energy in […]
Amino acids and Proteins
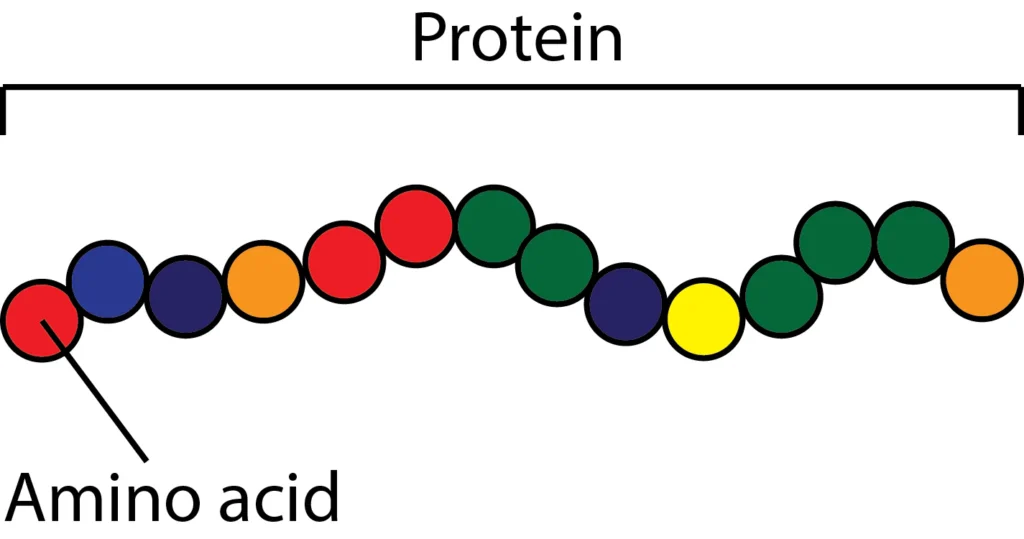
Proteins are made up of amino acids. It consists of C, H, N, O and other elements such as S, Fe, etc. Proteins are classified based upon their components such as simple and conjugated proteins as well as depending upon their axial ratio these are divided into globular and fibrous. When proteins dissociated by the […]
