Mass Spectroscopy
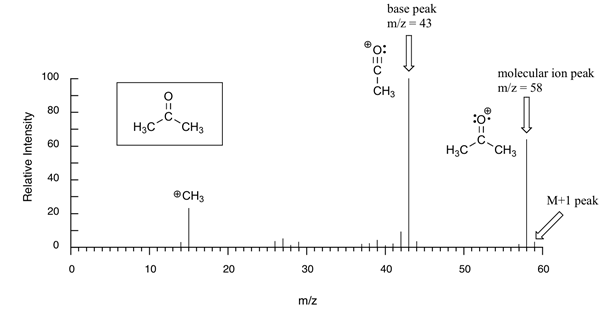
Mass Spectroscopy It is a spectrometry technique which is used to detect the molecular mass of the compound under analysis. When a sample is applied to mass spectrometry, it decomposes the sample into fragments and fragmented ions move according to their mass/charge ratio (m/e). The mass spectrum of each and every compound is different due […]
Paper Chromatography

Paper Chromatography It is a technique to differentiate and separate colored compounds. It is available in various types one is rotating paper chromatography in which paper is cut into a circle and two solvents are used to mark the different solvent front. It contains three things, the mobile phase, stationary phase, and chamber. The mobile […]
Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)

Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) TLC is thin layer chromatography which is found to be the best and easy method of separation of compounds present in the sample. To detect the purity of the sample and quantity it is one of the reliable methods. It consists of a mobile phase that can be solvent, a stationary […]
HPLC

HPLC It is a column chromatography which is known as high-performance liquid chromatography or high pressure/ priced liquid chromatography. It can be applied to both volatile as well as non-volatile liquid. It can be used to analyze qualitative as well as quantitative methods of detection. It is based on the principle of partition and adsorption. […]
Gas Chromatography

Gas Chromatography Gas chromatography is also a technique of identifying and isolating a molecule based on its vaporization without any decomposition. Although, the prominent use of this technique is to purify and separating a compound. Moreover, it can be utilized for preparative methods. The mobile phase in gas Chromatography is usually a gas carrier that […]
Re-crystallization
Re-Crystallization It is a technique used in chemistry to purify a compound by dissolving the smaller crystals and impurities present into it in a suitable solvent. But there is one important thing to be considered is that there should be a difference in the solubility of product and impurity in the selected solvent for re-crystallization. […]
Distillation
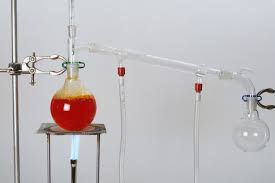
Distillation Distillation is used to separate the pure chemical out of the liquid mixture. First evaporation takes place than condensation. The basic principle of distillation is the use of temperature based upon the temperature difference between the liquids gets separated. There many types of distillation: Simple Distillation Flash Distillation Vacuum Distillation Steam Distillation Molecular Distillation […]
Sublimation
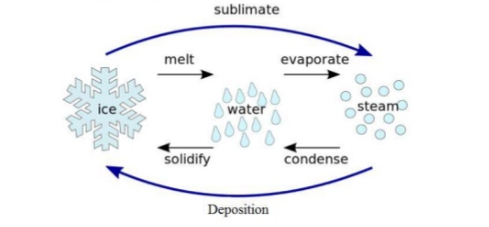
Sublimation It is a process in which a solid substance is directly converted into the gas phase, skipping the liquid phase. It is an endothermic process in which pressure and temperature are below the triple point of substance. Reversing the sublimation process is known as desublimation. The term sublimation is used to give an idea […]
Covalent Bond
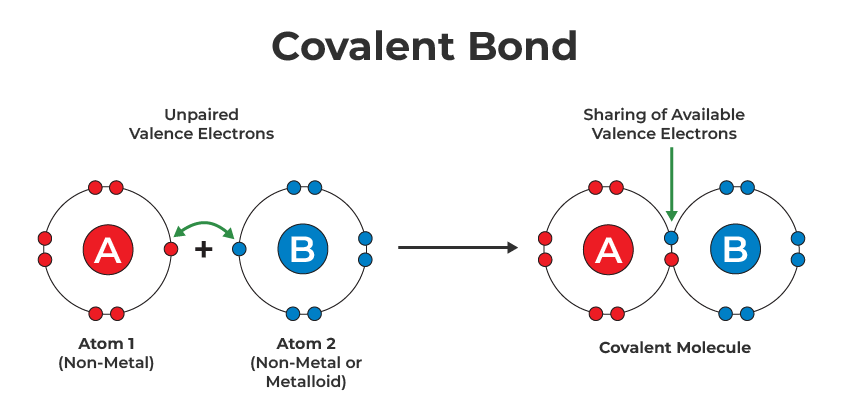
Covalent Bond Covalent bonding is a chemical bonding that takes place between atom which shares their electron pair/shared pair/ bonding pairs. It is formed when a stable balance between repulsive and attractive forces takes place. This type of bonding allows each atom participating to attain full configuration. These types of bonding are very common […]
Ionic Bonds
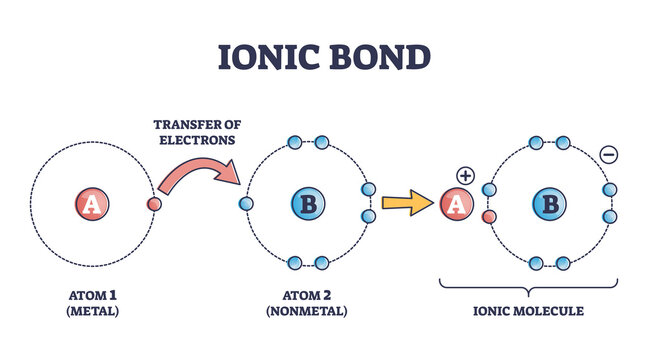
Ionic Bonds It is a type of chemical bonding that occurs between oppositely charged ions which involves electrostatic forces. This bonding is the first interaction between the ions. Anions are negatively charged ions that have gained an electron. On the other hand, cations are those ions that contain positive charge after losing an electron. In […]
