Methane
Methane is the smallest member of the alkane family as well as all of the organic compounds. Yet, It is the most important and powerful of gases on the planet. It is formed by the anaerobic decay of plants and is a major constituent of the natural gas. It can be obtained as a pure form by fractional distillation of natural gas.
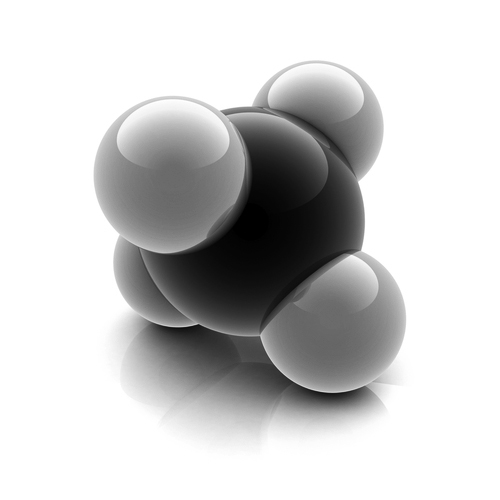
One carbon atom is bonded to four hydrogen atoms by sharing of electrons, i.e., through covalent bonding. Bonding orbitals are formed by mixing one s and three p-orbitals leading to sp3 hybridization. The shape of the molecules is tetrahedral in nature with an angle of 109.5° so that the atoms can arrange themselves as far as possible from each other.
Structure of methane is as follows,
 It is a colorless, odorless gas with a melting point of -183 °C and a boiling point of -161.5 °C. Liquid methane is less dense than water. It is very slightly soluble in water but highly soluble in organic liquids such as ether, alcohol, and gasoline. It is highly flammable in nature.
Methane is one of the major sources of electricity generation and for manufacturing of organic chemicals. It is a powerful greenhouse gas than even carbon dioxide and contributing to about 25 % of the man-made global warming.
It is a colorless, odorless gas with a melting point of -183 °C and a boiling point of -161.5 °C. Liquid methane is less dense than water. It is very slightly soluble in water but highly soluble in organic liquids such as ether, alcohol, and gasoline. It is highly flammable in nature.
Methane is one of the major sources of electricity generation and for manufacturing of organic chemicals. It is a powerful greenhouse gas than even carbon dioxide and contributing to about 25 % of the man-made global warming.
 It is a colorless, odorless gas with a melting point of -183 °C and a boiling point of -161.5 °C. Liquid methane is less dense than water. It is very slightly soluble in water but highly soluble in organic liquids such as ether, alcohol, and gasoline. It is highly flammable in nature.
Methane is one of the major sources of electricity generation and for manufacturing of organic chemicals. It is a powerful greenhouse gas than even carbon dioxide and contributing to about 25 % of the man-made global warming.
It is a colorless, odorless gas with a melting point of -183 °C and a boiling point of -161.5 °C. Liquid methane is less dense than water. It is very slightly soluble in water but highly soluble in organic liquids such as ether, alcohol, and gasoline. It is highly flammable in nature.
Methane is one of the major sources of electricity generation and for manufacturing of organic chemicals. It is a powerful greenhouse gas than even carbon dioxide and contributing to about 25 % of the man-made global warming.