Lipids
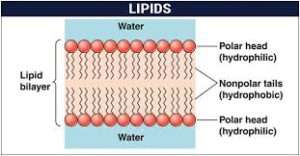
Lipids are the heterogeneous compounds which are made up of fatty acids. Lipids are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents like chloroform, ether, benzene, etc. These are nonpolar in nature. These are classified as waxes, glycolipids, acylglycerols, terpenoids, and sphingolipids.
History:
Lipids are regarded as a major concentrated storage form of energy in the body. In the early 18th century, lipids are classified into suifs and huils but in 1823, Micgel Eugene gave a wide classification of lipids such as waxes, resins, balsams, tallow, volatile oils, greases, etc. Pelouz TJ in 1844, got success in synthesizing tributyrin. After him one of his students, synthesize tristearin.
In 1827, William Prout gave an idea about a mixture of fats along with proteins and carbohydrates. For a long time lipids are known as fats but in 1847 Theodore Gobley found phospholipids in the human brain and egg, after that he called it lecithins.
Advantage:
- Lipids are the starting materials of many components.
- The lipoidal membrane maintains the functional and structural integrity of organs.
- Lipoidal barrier preserves and protects temperature changes in the body.
- Regulation of hormones.
- Transport of cellular signals.
Disadvantage:
- Saturated fat consumption cause damage to the heart.
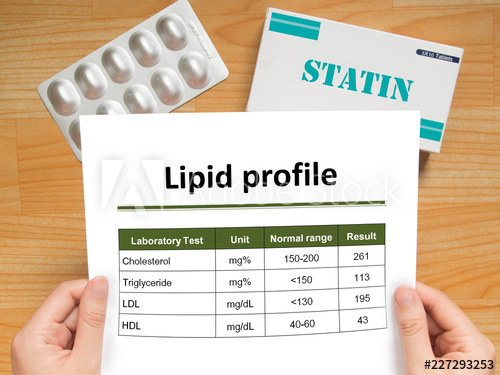
- Hydrogenated fats decrease good cholesterol levels and increase LDL in the body.
- Fats are not easily metabolized in the body and stay for a longer period of time.
- It can cause liver malfunctioning, obesity.