Diels-Alder Reaction
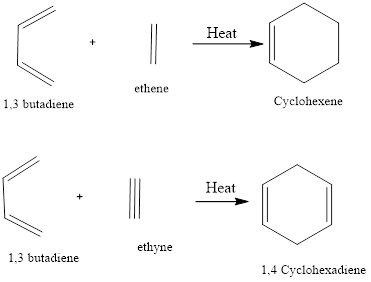
Diels – Alder Reaction Diel-Alder reaction is a type of cycloaddition reaction. There is cycloaddition of a conjugated diene with an alkene to form cyclohexene. The reaction was first discovered by Otto-Diels and Kurt Alder in the year 1928 and their work was applauded with Nobel Prize in chemistry in the year 1950. There is […]
Wurtz Reaction
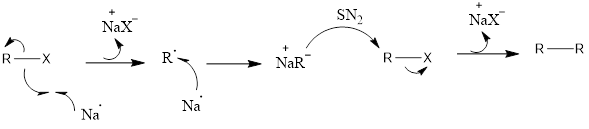
Wurtz Reaction It is an organometallic reaction which leads to the formation of alkanes by coupling of two alkyl halides in presence of sodium metal. The reaction was discovered by Charles- Adolphe Wurtz in 1855. Mechanism of action: It is a reaction which involves free radical formation. Firstly there is single electron transfer, sodium metal […]
Sandmeyer Reaction
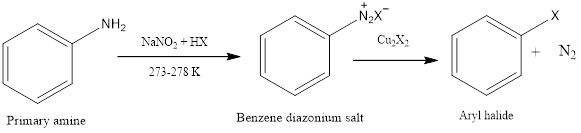
Sandmeyer Reaction Sandmeyer reaction is a nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction in which benzene diazonium salt is converted to aryl halide in presence of copper halide. The reaction was first discovered by Traugott Sandmeyer who was a Swiss chemist in the year 1804. Diazonium salt is formed in presence of sodium nitrite and cold aqueous mineral […]
Mannich Reaction
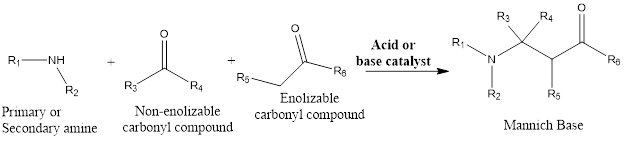
Mannich Reaction The mannich reaction is an organic amino alkylation reaction which leads to the formation of a β-aminocarbonyl compound from primary or secondary amine and carbonyl compounds from which one should be enolizable and other the other one should be non-enolizable. The reaction takes place in presence of base or acid catalyst. The reaction […]
Reimer-Tiemann Reaction
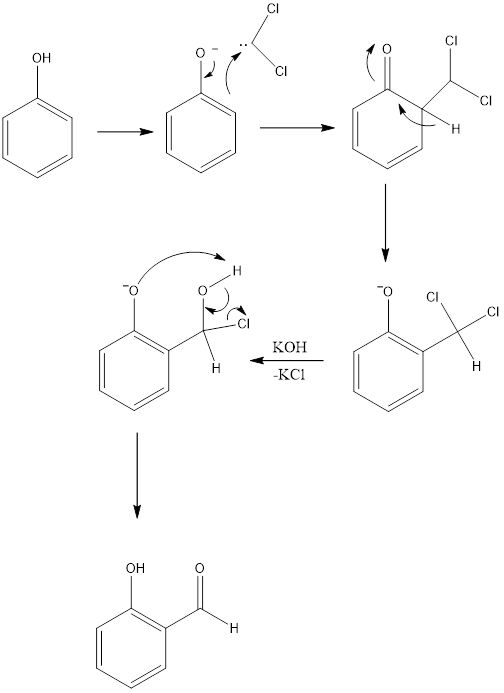
Reimer – Tiemann Reaction Reimer- Tiemann reaction is an organic reaction which forms hydroxybenzaldehyde from phenol in the presence of chloroform and base. The reaction is named after Karl Reimer and Ferdinand Tiemann who discovered reaction in 1876. The general reaction is the conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde. The reaction takes place in a biphasic […]
Clemmensen Reduction
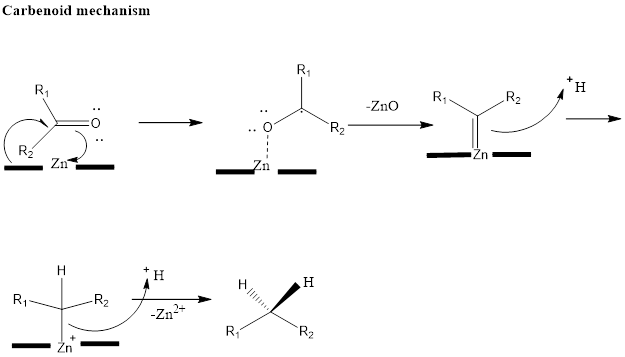
Clemmensen Reduction Clemmensen reduction is an organic reaction which leads to the formation of alkanes by reduction of aldehydes or ketones in presence of acid and with amalgamated zinc. The Danish chemist discovered this reaction named Erik Christian Clemmensen. The substrate should not be acid sensitive, if the substrate is acid sensitive then reduction is […]
Birch Reduction
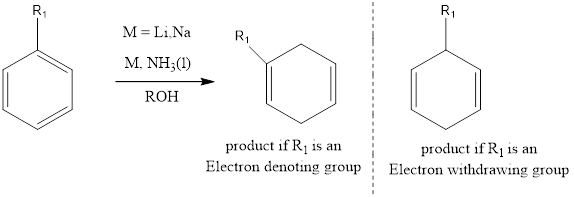
Birch Reduction It is an organic chemistry reaction where the benzene ring containing aromatic compounds undergoes 1,4 reduction to produce unconjugated 1,4 cyclohexadienes. The reaction was discovered by Australian chemist Arthur Birch in the year 1944. The reaction takes place in presence of metals like lithium, sodium or potassium in liquid ammonium along with alcohol. […]
Dieckmann Condensation
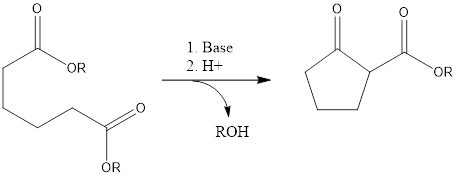
Dieckmann Condensation It is a ring-forming reaction to form cyclic β- keto ester by reaction of diesters with the base. It leads to the formation of 5- and 6-membered cyclic β-keto esters via intermolecular condensation in presence of a base. The reaction was discovered by German chemistry Walter Diekmann in 1894. The reaction has a […]
Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation
Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation It is the type of organic redox reaction to form ester or lactone from a ketone or cyclic ketone respectively. The reaction takes place in presence of peroxy acid, most commonly 3-chloroperoxybenzoic acid and trifluroperacetic acid are used.The reaction was first discovered by Adolf von Baeyer and Victor Villiger in the year 1899. […]
Yamaguchi Esterification
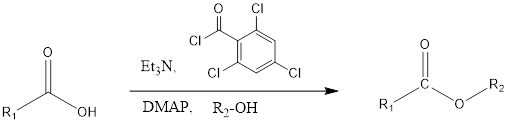
Yamaguchi Esterification The Yamaguchi esterification is the coupling organic chemistry reaction where the ester is formed from a carboxylic acid in presence of alcohol, triethylamine, 2,4-trichlorobenzoyl chloride i.e. Yamaguchi reagent and DMAP (4-Dimethylaminopyridine). The reaction was discovered in 1979 by Masaru Yamaguchi. Mechanism of action– Firstly carboxylic acid get deprotonated by triethylamine which results into […]
