Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation
It is the type of organic redox reaction to form ester or lactone from a ketone or cyclic ketone respectively. The reaction takes place in presence of peroxy acid, most commonly 3-chloroperoxybenzoic acid and trifluroperacetic acid are used. The reaction was first discovered by Adolf von Baeyer and Victor Villiger in the year 1899. They […]
Yamaguchi Esterification
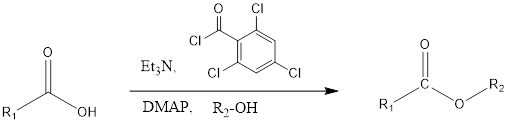
The Yamaguchi esterification is the coupling organic chemistry reaction where the ester is formed from a carboxylic acid in presence of alcohol, triethylamine, 2,4-trichlorobenzoyl chloride i.e. Yamaguchi reagent and DMAP (4-Dimethylaminopyridine). The reaction was discovered in 1979 by Masaru Yamaguchi. Mechanism of action– Firstly carboxylic acid get deprotonated by triethylamine which results into formation of […]
Atomic Orbital Vs. Molecular Orbital
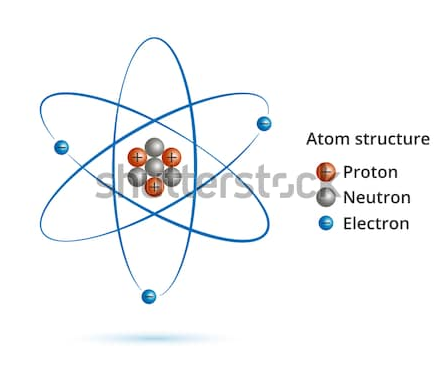
Atoms are building block and smallest part of the element which reacts chemically. Atoms consist of three fundamental particles i.e. electrons, protons, and neutrons. Charged particles, electrons they move around the nucleus in well-defined circular orbit. Atoms in the group are called as a molecule, a chemical bond is present which holds atoms in […]
Rate of Reaction

The rate of chemical reaction is the difference in concentration of reactant or product in unit time. It could be the rate of decrease in concentration of any one of the reactants or increase of rate in concentration in case of any one of the products. Reactant (R) Product (P) The rate of disappearance […]
Perkin Reaction
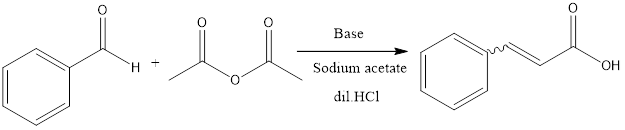
The Perkin reaction is a condensation reaction of organic chemistry. It involves the formation of α, β unsaturated carboxylic acid from aromatic aldehydes and anhydride in presence of a base catalyst which is alkali salt of the acid. The reaction was first discovered by William Henry Perkin in the 19th century, who was an English […]
Appel Reaction
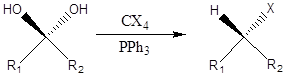
It is a type of the organic chemistry reaction to form alkyl halide directly by reaction of tetrahalomethane and triphenylphosphine and alcohol. The reaction was discovered in 1975 by Rolf Appel. Mechanism – Firstly in reaction triphenylphosphine and tetrachloromethane react to form phosphonium salt. Then deprotonation of alcohol occurs forming alkoxide followed by nucleophilic displacement, […]
Empirical and Molecular formula
A chemical compound is indicated in different ways in chemistry like by its common name, such as benzene or it can be indicated by its chemical formula. The chemical formula gives information of atoms specifically present in the chemical compound. The chemical formula is expressed as a molecular and empirical formula. In both of them, […]
Beckmann Rearrangement Reaction
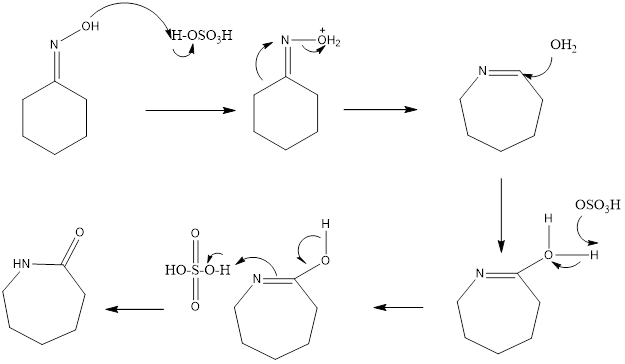
It is a rearrangement reaction in which oximes are converted into amides in presence of acid. The reaction was discovered by Ernst Otto Beckmann who was German chemist. The reaction is acid catalyzed, different acids can be used like polyphosphoric acid, sulfuric acid, hydrogen fluoride, acetic acid, and hydrochloric acid. Mostly sulfuric acid is employed […]
Schmidt Reaction
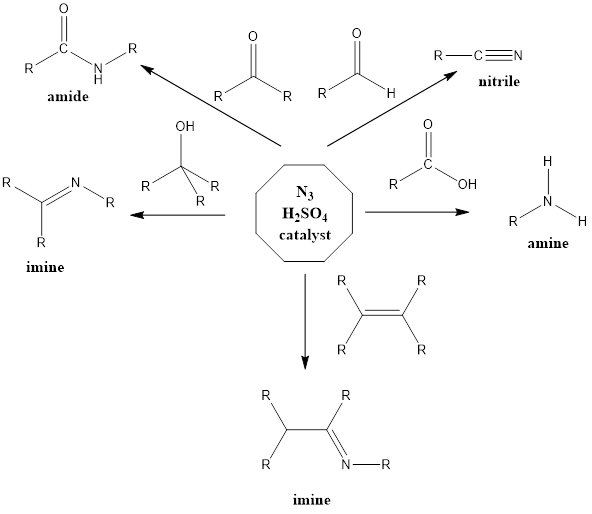
It is a rearrangement organic reaction where electrophiles like carbonyls, tertiary alcohols or alkenes react with hydrogen azide to form various products like amines, nitriles, amides or imines with the expulsion of nitrogen. The reaction was discovered by Karl Friedrich Schmidt in 1924 where benzanilide was successfully formed from benzophenone and hydrazoic acid. Reaction Mechanism […]
Hell-Volhard–Zelinsky Reaction
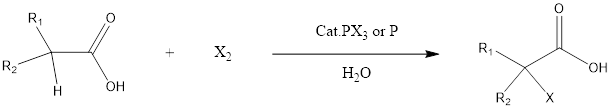
Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction is the substitution organic reaction which forms alpha halo carboxylic acid from a carboxylic acid having alpha hydrogen in presence of phosphorous halide or phosphorous as a catalyst. The reaction has been named after 3 chemists who discovered this reaction in a period of 1881-1887. The three chemists were Carl Magnus von Hell, […]