Retrosynthesis
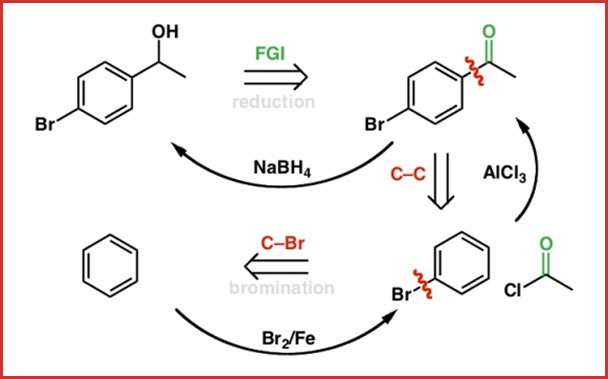
Retrosynthesis
Retrosynthesis is designing a reverse synthesis of the organic compound. This helps us to find the way of synthesis for that compound. Retrosynthesis give us an idea about the synthetic steps of a complex compound as well. Thus by Retrosynthesis, we can convert the target molecule into its simple precursors.
We are here to help you in designing Retrosynthesis of any organic molecule of your interest. Feel free to share your situation and goal related to this subject.
Upload Homework/Assignment

Online Organic Chemistry Tutor
FAQs about Retro-Synthesis
Highlight the importance of retrosynthesis in organic chemistry.
Retro synthesis is pivotal because it allows chemists to carefully and strategically plan synthetic routes for complicated compounds. Drug development, material science, and industrial chemistry chemists can create effective, affordable and practical methods for synthesizing desired chemicals by discovering simpler precursors.
Describe the key steps in retrosynthesis.
Determine the target molecule: This is done by defining the substance you want to create.
Disconnection: the target molecule is broken down into more basic precursor structures.
Functional Group Interconversion: is the process of changing the functional group to enable disconnections or access precursor structure is known as functional group interconversion.
Synthons and reagents: determine the real-world reagents that match the theoretical pieces.
What differentiates a synthetic equivalent from a synthon?
Synthon is an abstract representation of a fragment derived from the disconnection of a target molecule during retrosynthesis. On the other hand, the real chemical or reagent that can be utilized in a lab to produce the synthon during a forward synthesis is known as the synthetic equivalent.
Is it possible to apply retrosynthesis to any molecule?
Retrosynthesis can be applied to many molecules, particularly complex organic compounds. However, the molecule’s complexity, the accessibility of recognized reactions and reagents, and the chemist’s expertise affect its effectiveness. While many molecules may be designed synthetically with great effectiveness.
Describe the role of protecting groups in retrosynthesis.
In retrosynthesis, protective groups temporarily cover up reactive functional groups so they don’t experience unintended reactions at specific synthesis stages. This enables chemists to manipulate other molecular components selectively. After desirable modifications are achieved, protecting groups are removed to disclose the original functional group.
