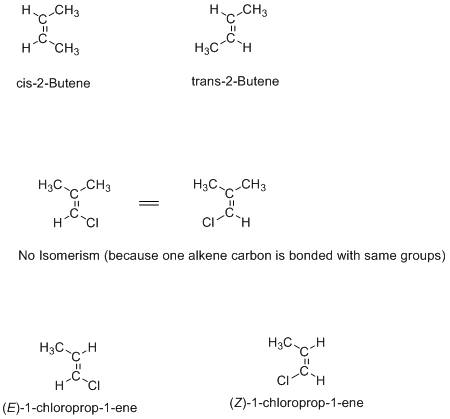
Geometric Isomerism
Geometric isomerism is shown by alkenes and cyclic compounds where rotation around the bond is not possible. These are normally defined as cis/trans or E/Z isomers.
Examples are given below:

Cis/trans terminology is used when the same type of substituents are attached to both double-bonded carbons, but when different groups attached to the both double-bonded carbons, then E/Z terminology is used (as shown in the figure). E (entagegen) means on opposite side, and Z (zusammen) means on the same side like trans and cis respectively.