Combinatorial Chemistry
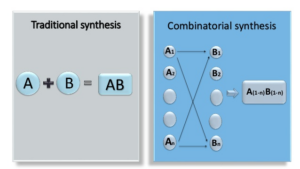
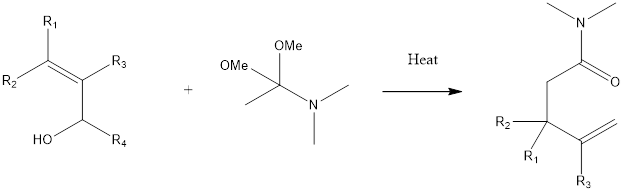
Combinatorial Chemistry is a new method developed to reduce the time and cost of producing effective, marketable and competitive new drugs. Combinatorial Chemistry is used to create large numbers of molecules that can be detected efficiently. This technique is useful in many areas such as Pharmaceutical chemistry, Biotechnology, and Agrochemistry. Combinatorial chemistry is a technique by which huge numbers of different but structurally similar molecules are produced rapidly and screened for pharmacological assay. In this technique, large numbers of analogs are produced using same reaction vessel and reaction conditions. By producing more diverse compound libraries, companies increase the probability that they will find novel compounds of significant therapeutic and commercial value. The combinatorial approach can give rise to millions of compound in same time compared to traditional method of synthesis which produces only one compound at a time.