Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopy
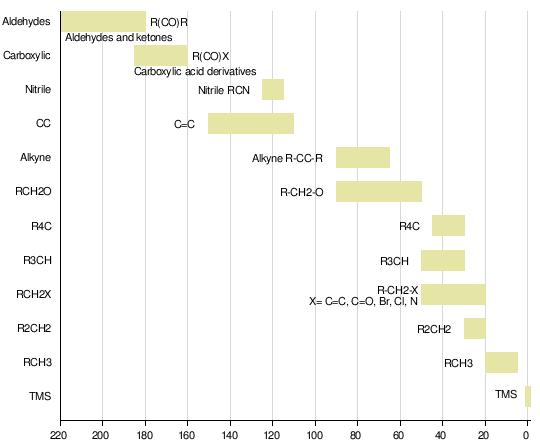
Nuclear magnetic resonance of C-13 is an advancement of NMR. It helps to detect carbon atom in a molecule or compound. A chemical shift in C-13 is as same as in proton NMR but it ranges from 0-220 ppm rather 0-12 ppm as in proton NMR. There is no carbon-carbon coupling in this spectroscopy because 13C occurs only 1.1% naturally. We also decouple the carbon-proton coupling to make the spectra simple and more useful.
Application:
- A non-invasive method which helps to analyze tissue samples.
- Due to the wide chemical shift, separation, and identification of metabolites.
- Easy to trace cellular metabolism.
- Purity and identification of drug samples.
- High molecular weight can be detected.
- Less sensitivity.
- The highly pure compound is required.
- Much time is required for analysis.