Markovnikov's Rule
Valadimir Markovnikov observed the pattern of halogenation of alkene where formations of two isomeric products are possible. Markovnikov rule state that in the addition of acid to carbon-carbon double bond of alkene, the hydrogen of acid attaches to the carbon that already holds a greater number of hydrogen.
It’s a regioselective reaction because the addition of acid to an alkene is at a specific position.
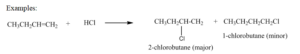
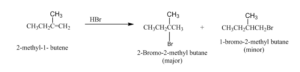
Examples:
 Mechanism:
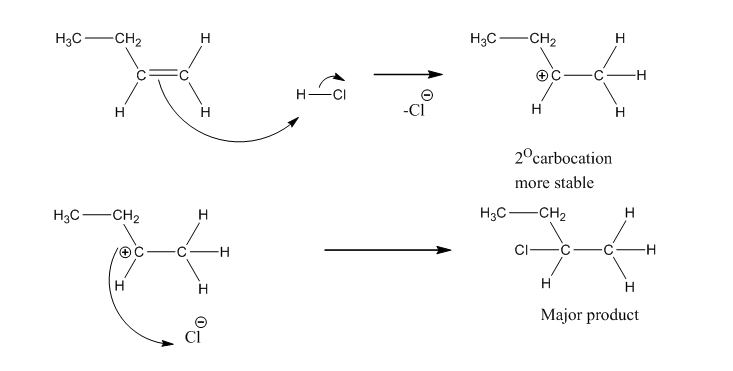
It’s an electrophilic addition and involves the formation of a carbocation. The more stable carbocation (3° > 2° > 1°) define the orientation of halide anion.
Mechanism:
It’s an electrophilic addition and involves the formation of a carbocation. The more stable carbocation (3° > 2° > 1°) define the orientation of halide anion.
 Mechanism:
It’s an electrophilic addition and involves the formation of a carbocation. The more stable carbocation (3° > 2° > 1°) define the orientation of halide anion.
Mechanism:
It’s an electrophilic addition and involves the formation of a carbocation. The more stable carbocation (3° > 2° > 1°) define the orientation of halide anion.