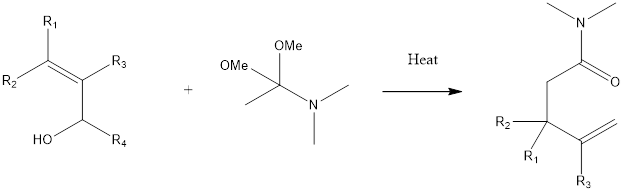
HPLC
It is a column chromatography which is known as high-performance liquid chromatography or high pressure/ priced liquid chromatography. It can be applied to both volatile as well as non-volatile liquid. It can be used to analyze qualitative as well as quantitative methods of detection.
It is based on the principle of partition and adsorption. Depending upon the stationary phase used. If the stationary phase is solid then adsorption phenomena, if it is liquid then the partition will be the principle.
 Types:
Types:
 Types:
Types:
- Normal phase: separation of compounds by taking polar stationary phase and polar mobile phase.
- Reversed-phase: separation of compounds by taking non-polar stationary phase and non-polar mobile phase.
- Adsorption: it is between the above two where moderately polar analyte separated by taking pure stationary phase such as alumina, silica.
- Ion-chromatography: organic or inorganic ions can be separated using the ionic stationary phase by Partitioning.
- Size-exclusion chromatography: if there are large molecules then they can be identified or separated based on their path taken through a maze tunnel.
- In biosynthesis studies, it is helpful to detect intermediate in biogenetic pathways and enzymes required.
- In microbiology, to control the process so that antibiotics can be separated from broth mixture.
- In synthetic reactions, to know the intermediate involved and targeted compound identification.
- To test hemoglobinopathies.
- Separation and purification of natural active substances.
- Costly technique as the instrument is highly sensitive.
- The complexity of the process.
- A well-trained person is required.