Specific Rotation
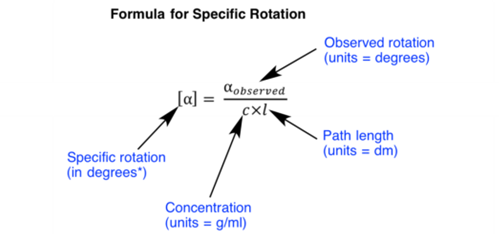
Specific rotation is characteristic value for every optically active compound. Observed rotation of a compound may vary as per variation in concentration and length of the sample tube, but the specific rotation is a constant value for every optically active compound. Following is a formula used for calculation of specific rotation:
Practice Question:
The concentration of a compound dissolved in water is 4.5 g per 100 mL of solution.
- A portion of this solution in a 5-cm Polarimeter tube causes an observed rotation of –1.4o. Calculate the specific rotation of that compound.
- Predict the observed rotation if the same solution were placed in a 10 cm tube.
- Predict the observed rotation if 10 mL of the solution were diluted to 20 mL and placed in a 5 cm tube.