Ionic Bonds
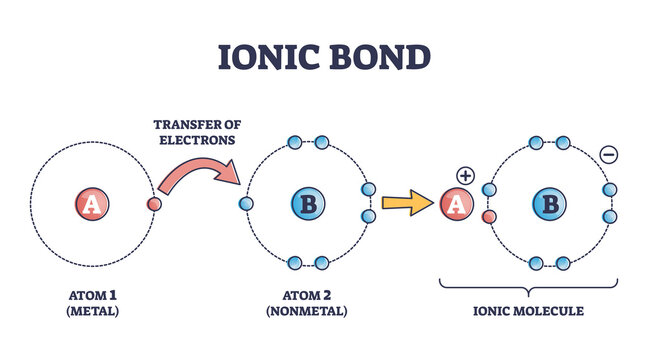
It is a type of chemical bonding that occurs between oppositely charged ions which involves electrostatic forces. This bonding is the first interaction between the ions. Anions are negatively charged ions that have gained an electron. On the other hand, cations are those ions that contain positive charge after losing an electron. In other words, […]
Hydrogen Bond

Hydrogen bonding is the electrostatic force of attraction and it occurs between hydrogen and more electronegative atoms (like F, N and O) and that too covalently bound atoms. Two atoms- one is hydrogen bond acceptor and other hydrogen bond donor. Fig: Water molecule showing intermolecular hydrogen bonding Hydrogen bonding is of two types: Intermolecular: it […]
Biginelli Reaction
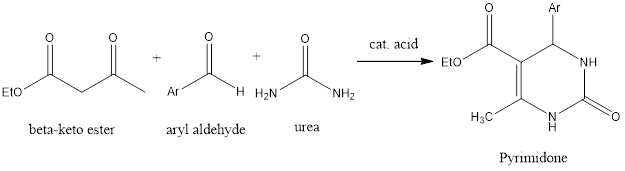
Biginelli reaction is ring forming organic chemistry reaction which forms pyrimidones from three components aldehyde, β-keto ester, and urea in the presence of acidic conditions. The reaction was discovered by Italian chemist Pietro Biginelli in 1891. Mechanism of reaction – Firstly, in reaction condensation of aldehyde and urea takes place, as it happens in Mannich […]
Eschweiler-Clarke Reaction
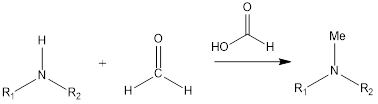
Eschweiler- Clarke reaction is a substitution type of reaction of organic chemistry that leads to the formation of tertiary methylamines by the reaction of primary amine or secondary amine in the presence of formaldehyde and formic acid. The reaction was discovered by German chemist Wilhelm Eschweiler as well as British chemist Hans Thacker Clarke. […]
Buchwald-Hartwig Amination
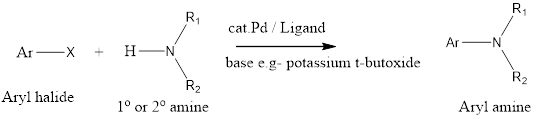
Buchwald-Hartwig amination is a cross-coupling organic chemistry reaction where aryl halide is coupled with an amine in the presence of a palladium catalyst and a strong base to form a carbon-nitrogen bond. The reaction has been discovered by Stephen L. Buchwald and John F. Hartwig in early 1983 and their work was first published in […]
Baylis-Hillman Reaction
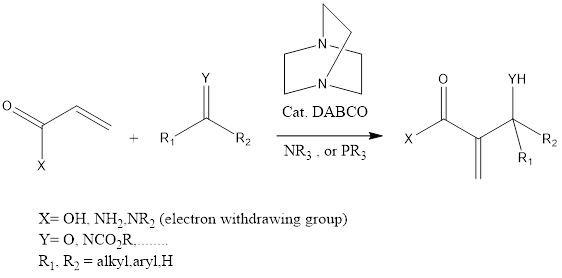
Baylis-Hillman reaction is a coupling organic chemistry reaction that leads to forming a C-C bond in between α, β carbonyl compounds like aldehyde or activated ketone and electrophiles. The reaction takes place in the presence of tertiary amine and phosphine and mostly DABCO (1,4 Diazabicyclo [2.2.2] octane tertiary amine is used. The reaction has […]
Hydroxychloroquine and COVID-19
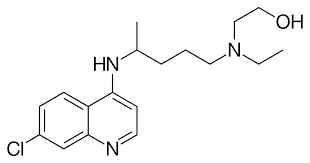
COVID-19 global spread took the lives of many people. It is a disease relate to the respiratory system induced by SARS-CoV-2[1]. WHO proposed to take preventive measures but simultaneously authorities also required clinical trials for drugs that are effective against the coronavirus. Although, fewer patients have access to clinical trials and it takes much time […]
Factors Affecting Chemical Shift in Proton NMR Spectroscopy
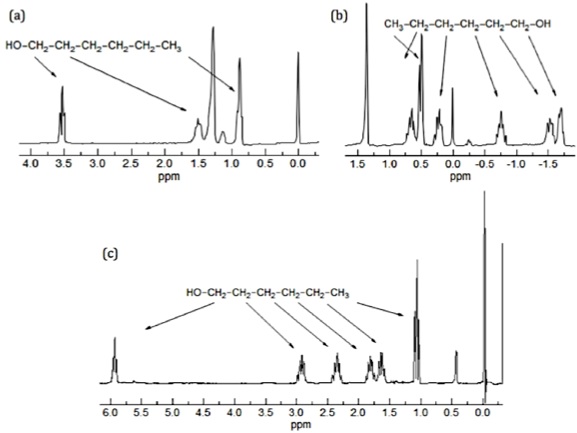
Electronegativity: more electronegative element leads to deshielding of protons and signal appears at downfield and vice versa. Anisotropy effect: those compounds which are having a double or triple bond involve pi-electron which produces an induced field that may change the position of electrons and hence lead to shielding or deshielding. Hydrogen bonding: it increases the […]
Retrosynthesis
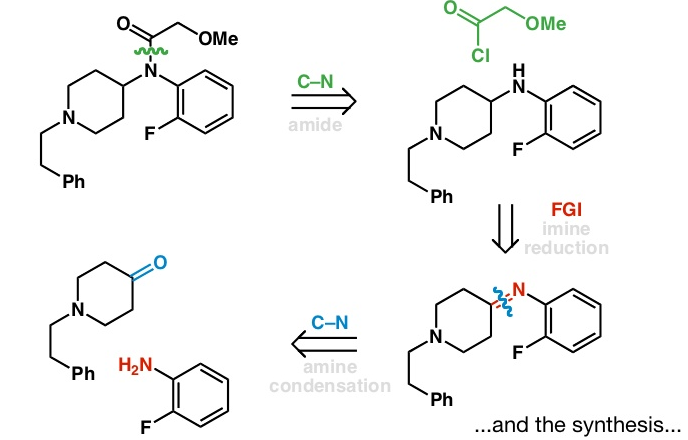
It is an analytical technique used in which the deconstruction or fragmentation of targeted organic molecule is done to produce starting material, generally called as “synthon”. Fragments generated via a particular pattern of break down. It is called as retro synthesis because it is a reversible process of chemical synthesis. E.J Corey gave this concept […]
NMR Signal Splitting
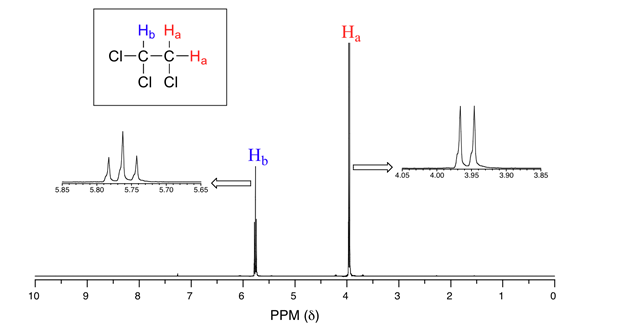
In NMR, the electric field is applied to the sample and the nearby proton aligned themselves in the same or different manner to the applied field. Splitting only happens between those protons of the same carbon which are not chemically equal to each other. Two magnetic fields felt by the proton due to which proton […]