UV-Visible Spectroscopy
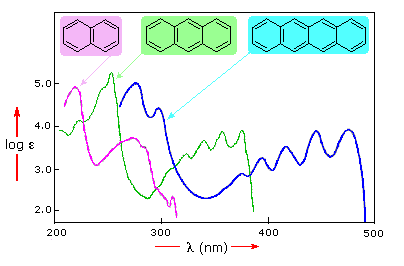
Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy is a technique used for structure elucidation of organic compounds. This technique is majorly used for identifying conjugated dienes, polyenes, unsaturated carbonyl compounds and aromatic compounds. Aliphatic organic compounds do not show any absorption peak in this region. With the help of Woodward Fieser Rules, we can predict the absorption maximum of compounds […]
Infrared Spectroscopy
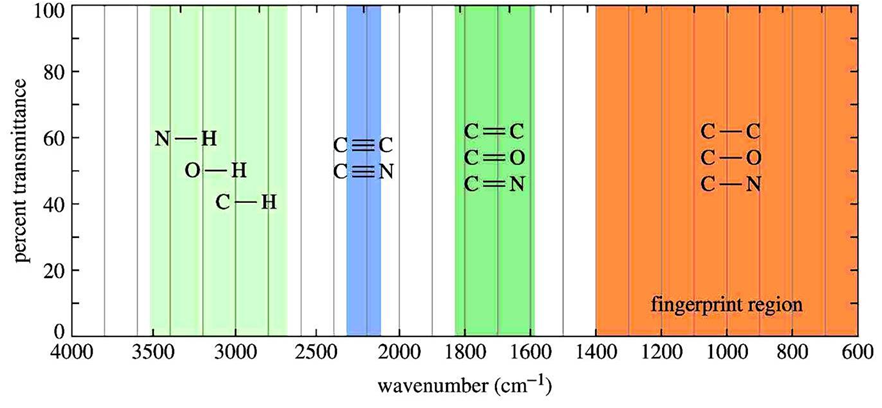
Infrared spectroscopy is a technique for identifying different possible functional groups of organic compounds. Infrared spectra can be divided into two parts one is functional group region and other is fingerprint region. If the organic compounds are from the same family as methanol, ethanol, propanol, etc. then functional group region will give peaks at the […]
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
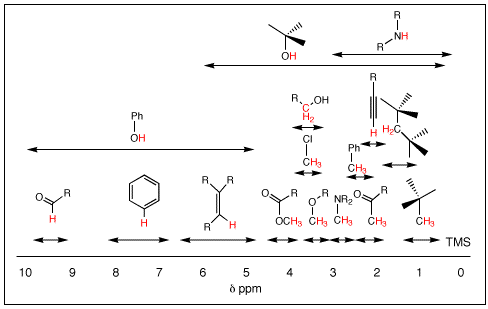
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) is most effective and efficient technique in structure elucidation of unknown organic compounds. There are various types of NMR techniques like proton, carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus NMR but among them, 1H-NMR is most common and widely used to get an idea of hydrogens and their exact location in the organic […]
Mass Spectroscopy
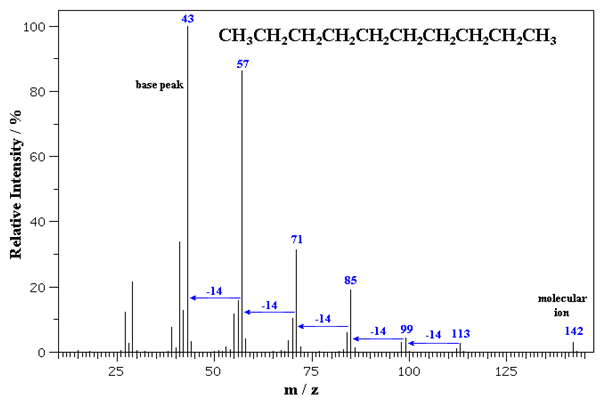
Mass spectroscopy is a technique for structure elucidation of unknown organic compounds which basically gives the idea of the molecular mass of the compound by molecular ion peak. This molecular ion peak (M+) comes at the extreme right of the mass spectra. There is another important peak known as base ion peak which due to […]
PROCHIRALITY
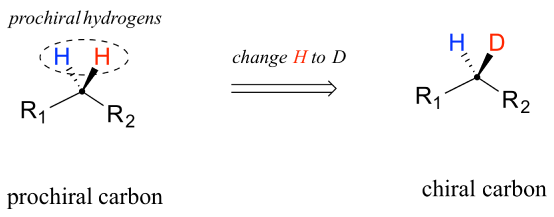
Prochiral molecules are generally represented as Pro-R or Pro-S, and these are the precursors of chiral molecules which can be converted into chiral molecule from Prochiral in a single step. Prochirality can be observed in organic compounds in two ways, one way is the conversion of sp2 carbon into a chiral sp3 carbon via a […]
Combinatorial Chemistry
Combinatorial Chemistry is a new method developed to reduce the time and cost of producing effective, marketable and competitive new drugs. Combinatorial Chemistry is used to create large numbers of molecules that can be detected efficiently. This technique is useful in many areas such as Pharmaceutical chemistry, Biotechnology, and Agrochemistry. Combinatorial chemistry is a technique […]
Acid Strength

Acid strength depends on atom’s capacity to accommodate the electron pair left behind by the departing hydrogen ion. There are basically two factors which affect the atom’s ability of accommodation of electron pair that is electronegativity and size. If we move within a row (from left to right) of periodic table acidity increases due to […]
Acidity of Alkynes
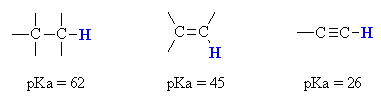
Terminal alkynes show acidity due to terminal hydrogen atom which can be easily abstracted by a strong base like sodium amide (NaNH2). Terminal alkynes show acidity compared to other hydrocarbons due to more ‘s’ character of terminal carbon which is sp hybridized. Due to more ‘s’ character, it withdraws the electron of terminal hydrogen attached […]
Enantiomeric Excess (ee)

When there is a chiral center in a molecule, there is a possibility of the enantiomeric mixture, which contains both dextro and levorotatory isomers but if these isomers in equal amount in a mixture that is named as a racemic mixture which contains 50-50% of both enantiomers. This mixture remains optically inactive because 50% molecules […]
Stability Order of Carbocation, Carbanion and Free Radicals

Stability order of carbocations increases as we move from primary to tertiary cation due to +I effect of methyl groups there is a redistribution of positive charge all over the molecule which reduces the intensity of positive charge on central carbon and increases the stability of the molecule. Stability order of carbanions decreases as we […]